COVID-19 Impact
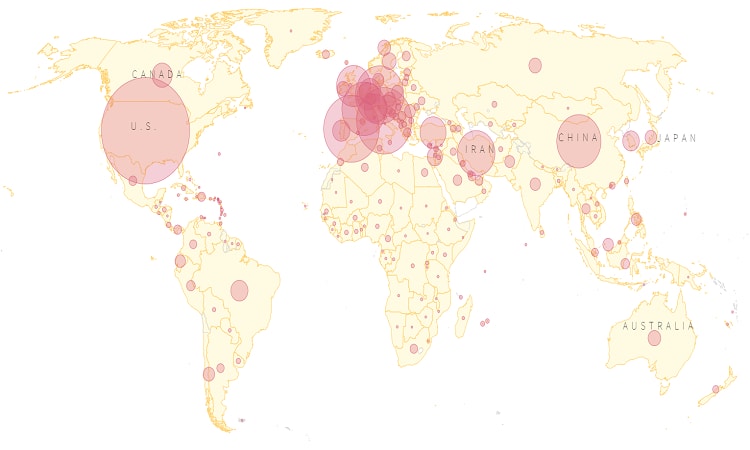
The first case of coronavirus can be traced back to November 17, 2019. A 55-year-old from Hubei in Wuhan, China was the first person to be infected with this deadly virus. Since then the number of coronavirus cases have been piling up and now COVID-19 has taken a toll over the globe. The total number of coronavirus cases across the globe has risen to 1,320,000 with 74,300 deaths. Who knew that this virus would turn out to be a pandemic, claiming lives of thousands of people. COVID-19 pandemic has massively affected the global economy.
The global economy is so drastically hit by the coronavirus pandemic that it could shrink by up to 1 percent in 2020. The United Nations has also stated it might contract even further if the restrictions on economic activities are extended without sufficient fiscal responses. Over 100 countries have closed their national borders that have a huge impact on the travel & tourism industry. Analysis by the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) have shown that this ongoing pandemic is also disrupting global supply chains and international trade.
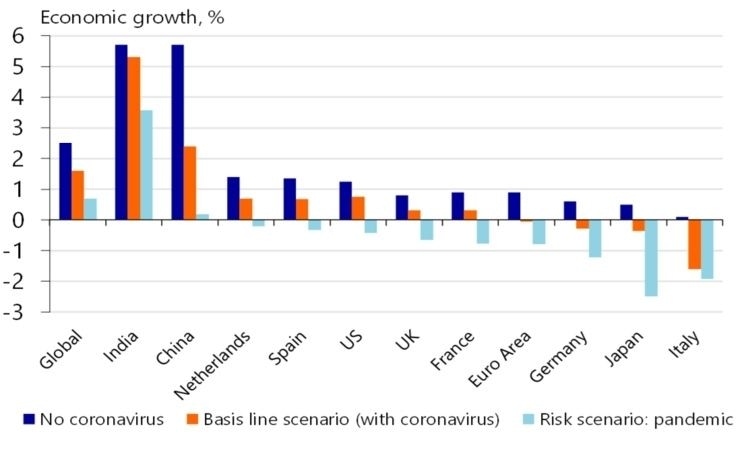
Thousands of people in the countries are losing their jobs. If we see the situation in India then the majority of the population of India are daily wage workers which are massively hit by the COVID-19 economic crisis. To avert a sharp downturn of the economies, the government is rolling out large packages to curb the deep recession. In addition to this, the government is also providing meals to the poor and needy people for their basic survival as they are the ones who are hardest hit. Do read the blog Free Meals to know the steps taken by the railway board to curb hunger. The UN studies have also added that the contraction could be even higher if the government fails to provide income support to its people.
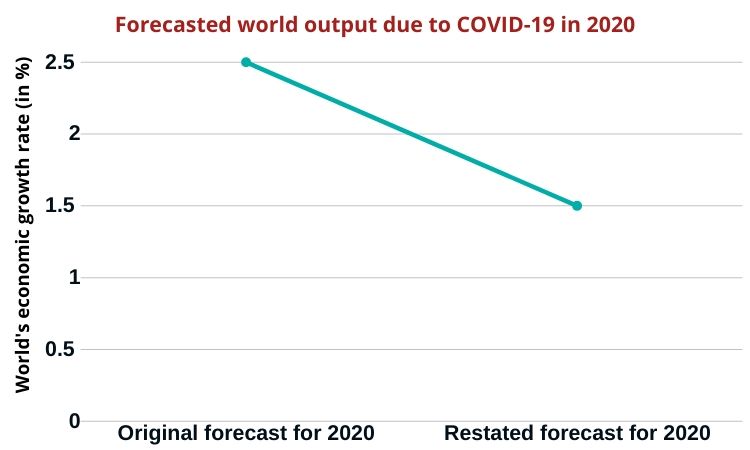
As per the reports of the World Economic Situation and Prospects 2020, world output was expected to increase by 2.5 percent in 2020 before the outbreak of COVID-19. Lockdowns in Europe, America and Asia are hitting the service sector hard particularly industries that require physical interaction like retail trade, hospitality, leisure, recreational, travel & tourism ad transportation services. As service sector industries incur a huge loss of revenue, unemployment is likely to increase throughout the economy.
Such an impact of COVID-19 pandemic calls for bold policy measures not only to contain the spread of novel coronavirus but also to sustain economic growth and financial stability. It also warns us that the adverse effects of prolonged economic restrictions in developed economies would soon spill over through trade and investment. Developing or developed countries that are largely dependent on tourism and export of goods are at the forefront of economic risk. At the same time, decline in commodity-related revenues is increasing the debt distress in many nations. UN Chief Economist and Assistant Secretary-General for Economic Development Elliot Harris said that the collective goal should be a resilient recovery as it is the only way to put the planet back on sustainable development.
1918 Pandemic and its impact
A similar pandemic occurred in 1918 called as Spanish flu (Influenza) that was the deadliest in recent history. It was caused by an H1N1 virus with genes of avian origin. Spanish flu caused a global pandemic spreading rapidly and killing indiscriminately. Young, old, sick all became infected. It is estimated that influenza has infected over 500 million people worldwide—about one-third of the planet’s population and has killed 20 to 50 million people. Spanish flu was first observed in Europe. During these times there were no effective drugs or vaccines available to treat the deadly flu.
A similar pandemic occurred in 1918 called as Spanish flu (Influenza) that was the deadliest in recent history. It was caused by an H1N1 virus with genes of avian origin. Spanish flu caused a global pandemic spreading rapidly and killing indiscriminately. Young, old, sick all became infected. It is estimated that influenza has infected over 500 million people worldwide—about one-third of the planet’s population and has killed 20 to 50 million people. Spanish flu was first observed in Europe. During these times there were no effective drugs or vaccines available to treat the deadly flu.
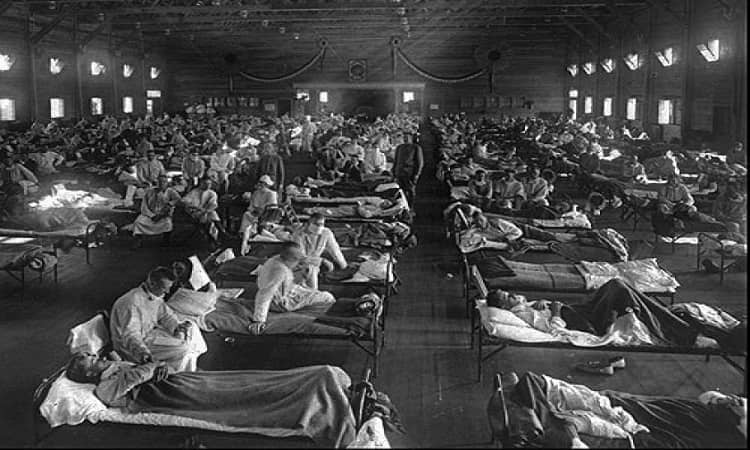
The flu pandemic came to an end by the summer of 1919. Around 90 years later in 2008, researchers came to know about the group of three genes that made the flu so deadly. Since 1918, there have been countless other influenza pandemics, though none as deadly as spanish flu. A flu pandemic from 1957 to 1958 killed around 2 million people worldwide, including some 70,000 people in the United States, and a pandemic from 1968 to 1969 killed approximately 1 million people, including some 34,000 Americans.
That’s all for today. Stay home, stay safe. Let's just hope that everything gets back to normal soon. Till then keep reading the Trainman blog to know the latest updates on railways and COVID-19 virus. Trainman advises all its users to self-isolate themselves in the wake of COVID-19




0 Comments